

It was known that electrons could be removed from atoms, and that they became positive ions as a result. With the combined results of Thomson and Millikan, a value for the electron mass was obtained - a value far below that of atoms. The determination of the charge of the electron awaited the work of Millikan who measured the electron charge in 1909 with his oil drop experiment.

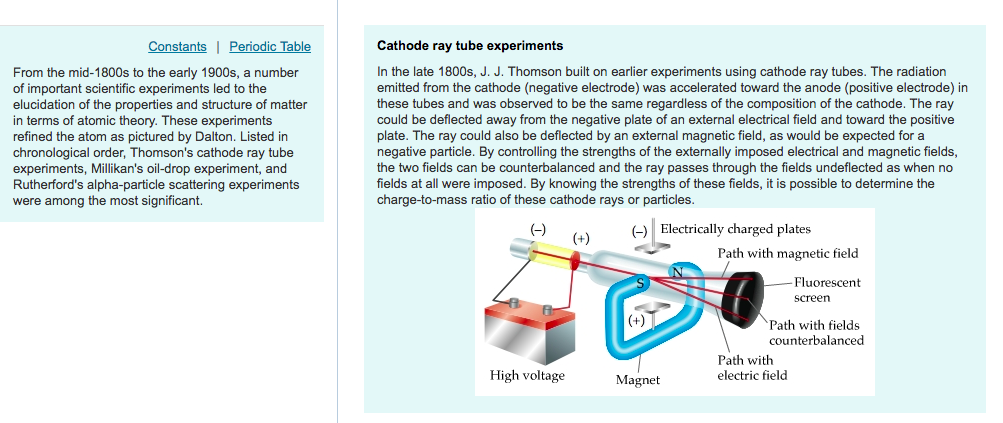
Using this apparatus, Thomson determined the charge-to-mass ratio of the electron, e/m. This same principle is presently used in velocity selectors for mass spectrometers. J. Thomson, Cathode rays (Friday evening meeting of the. Thomson wanted to see if, by bending the rays with a magnet, he could separate the. Background Information: A debate about whether cathode rays were electromagnetic waves or streams of charged particles was unsolved as cathode rays behaved. J.J Thomson used this to predict the mass of an electron and. Thomson showed that with the application of both electric and magnetic fields, he could balance the deflections and obtain a straight beam. his corpuscle hypothesis, and in section 4 I discuss the experiments of 1897. Perrin had discovered that the cathode rays deposited a negative charge. The Cathode ray tube is a device which uses electrons being fired through a vacuum onto a screen. A narrow luminous beam could be produced by using an aperture near the cathode, and this beam could be deflected by either an electric field or a magnetic field. In the 1890's, cathode ray tubes had been developed in which a luminous beam could be produced in a partially evacuated glass tube, directed from the negative electrode (cathode) to the positive (anode). Thomson theorized that the traces of gas remaining in the tube were being turned into an electrical conductor by the cathode rays themselves, and managed to. Sir Joseph John Thomson (1856-1940) played a pivotal role in developing our understanding of the electron.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
